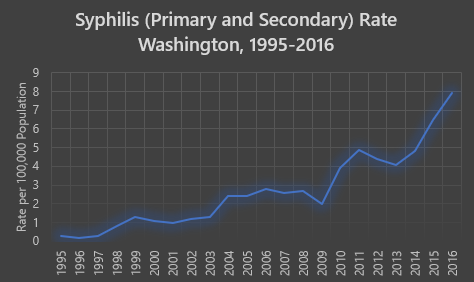
Tuberculosis Screening

Consider testing Person traveling in TB endemic areas. Migrant workers. Person experiencing homelessness. Contact to a tuberculosis case. Foreign-born person from tuberculosis-endemic area. Person who injects drugs. Immunosupressed person (e.g., HIV positive or organ transplant). Resident/employee of healthcare, correctional or long-term care facility. Person with chronic medical problem (e.g., diabetes, end stage renal disease). Test … Tuberculosis Screening